### Understanding AC Generators:
The Backbone of Electrical Power Generation
Alternating Current (AC) generators, also known as alternators, are essential devices used to convert mechanical energy into electrical energy in the form of alternating current. These generators play a crucial role in providing the electrical power that fuels homes, industries, and businesses worldwide.
#### What is an AC Generator?
An AC generator is a machine that produces alternating current by utilizing the principle of electromagnetic induction. The basic mechanism involves rotating a coil of wire within a magnetic field, which induces an electrical current in the coil. The direction of the induced current alternates as the coil rotates, creating the alternating current.
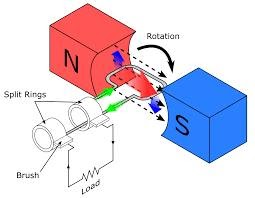
The essential components of an AC generator are:
1. **Armature (Rotor):**
A coil of wire that rotates within the magnetic field.
2. **Magnetic Field (Stator):**
A fixed magnet or a set of electromagnets that create a magnetic field in which the armature rotates.
3. **Slip Rings:**
These are used to maintain continuous electrical contact with the rotating armature, allowing the alternating current to flow out of the generator.
4. **Brushes:**
These are in contact with the slip rings, allowing the current generated in the armature to be transferred to the external circuit.
#### How Does an AC Generator Work?
The operation of an AC generator is based on **Faraday’s Law of Electromagnetic Induction**,
which states that a voltage (or electromotive force, EMF) is induced in a conductor when it moves through a magnetic field.
1. **Magnetic Field Interaction:**
When the armature, a coil of wire, rotates in the presence of a magnetic field, the motion of the coil causes the magnetic flux passing through the coil to change.
2. **Induced Current:**
According to Faraday's Law, this change in magnetic flux induces an electromotive force (EMF) in the coil. The induced EMF causes a flow of electric charge, creating an electric current.
3. **Alternating Current Generation:**
As the armature continues to rotate, the direction of the induced EMF changes because the magnetic field constantly shifts relative to the coil. This results in the alternating current (AC) that flows out of the generator.
The speed at which the armature rotates determines the frequency of the generated AC, while the strength of the magnetic field influences the voltage produced.
#### Types of AC Generators
1. **Synchronous Generators:**
These generators operate at a constant speed, meaning the rotor rotates at the same speed as the rotating magnetic field produced by the stator. They are used in large power plants and industrial applications.
2. **Asynchronous (Induction) Generators:**
These generators operate at a speed slightly different from the synchronous speed. They are commonly used in smaller-scale applications, such as wind turbines.
#### Applications of AC Generators
AC generators are ubiquitous in modern society. Some key applications include:
**Power Plants:**
AC generators are the primary source of electricity generation in power plants. They are driven by turbines powered by steam, water, or wind.
**Transportation:**
AC generators are used in vehicles such as cars, buses, and trains to provide electrical power for lights, air conditioning, and other systems.
**Portable Generators:**
Smaller AC generators provide backup power in residential and commercial settings during outages.
**Industrial Use:**
Large machines and factories often rely on AC generators for running heavy machinery and other equipment.
#### Advantages of AC Generators
**Efficiency in Power Transmission:**
AC can be easily stepped up to high voltages, making it more efficient for long-distance power transmission. High-voltage AC reduces energy losses during transmission.
**Cost-Effective:**
AC generators are relatively simple and cost-effective to build and maintain, making them a widely used technology.
**Versatility:**
AC generators can be used in a variety of applications, from large-scale power plants to small, portable generators.
#### Conclusion
AC generators are vital devices in the world of electrical engineering, providing the means to generate and supply electrical power on a massive scale. Their ability to efficiently convert mechanical energy into alternating current has made them indispensable in both large power plants and everyday applications. As the demand for electricity continues to grow, AC generators will remain a cornerstone of global power generation systems.




No comments:
Post a Comment